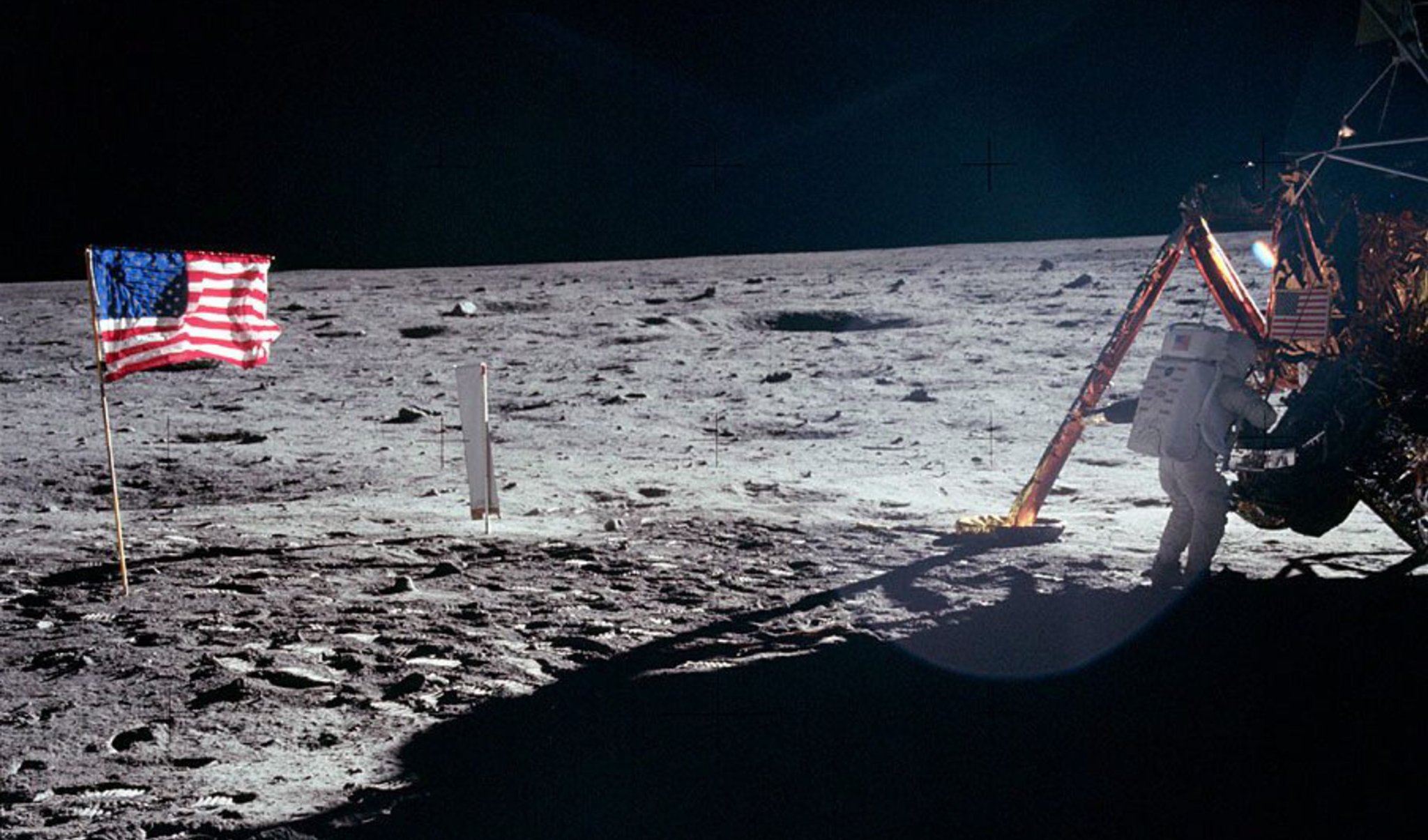
The Moon landing is one of humanity's most remarkable achievements, capturing the imagination of millions around the globe. On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to set foot on the lunar surface, marking a pivotal moment in the history of space exploration. This monumental event, broadcast live to a captivated audience, represented the culmination of years of scientific endeavor and exploration, showcasing mankind's tenacity and ambition. The phrase "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind" echoed throughout the world, encapsulating the triumph of human spirit and ingenuity.
The Apollo 11 mission, spearheaded by NASA, was the culmination of intense competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, known as the Space Race. It was a period marked by significant technological advancements and scientific discoveries, all driven by the desire to achieve the seemingly impossible—landing a man on the moon. This race to the moon was not merely a quest for technological prowess but a symbol of national pride and a testament to the power of human innovation. The mission's success was a defining moment in the 20th century, changing the course of space exploration forever.
Beyond its historical significance, the moon landing had profound implications for science and technology. It spurred further exploration and research, leading to numerous scientific breakthroughs and technological advancements that continue to benefit humanity today. From the development of new materials to advancements in telecommunications and computing, the legacy of the moon landing is evident in many aspects of modern life. This article delves into the details of the moon landing, exploring its background, the mission itself, and its lasting impact on science and society.
Read also:All About Carrie Underwood Pregnancy A Detailed Analysis And Insights
Table of Contents
- Background of the Moon Landing
- How Did the Space Race Intensify?
- The Apollo 11 Mission: A Closer Look
- Who Were the Crew Behind the Moon Landing?
- What Happened When Man Stepped on the Lunar Surface?
- Technological Advancements from the Moon Landing
- Impact on Space Exploration and Beyond
- The Lasting Legacy of the Moon Landing
- Are There Moon Landing Conspiracy Theories?
- How Did the Moon Landing Influence Education and Science?
- When Are Moon Landing Anniversaries Celebrated?
- What Does the Future Hold for Moon Missions?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Background of the Moon Landing
The journey to the moon landing was not an overnight success but a series of methodical steps and scientific advancements. The origins of this ambitious project can be traced back to the early days of the space race, following the launch of Sputnik by the Soviet Union in 1957. This event marked the beginning of an intense rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union for supremacy in space exploration. The United States, driven by a desire to assert its technological and ideological superiority, vowed to not only catch up with but surpass the Soviet Union's achievements in space.
The significance of the moon landing was underscored by President John F. Kennedy's famous speech in 1961, in which he declared that the United States would land a man on the moon and return him safely to Earth before the decade's end. This bold proclamation galvanized the nation, leading to increased funding and resources dedicated to the development of space technology. NASA, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, was at the forefront of this effort, spearheading the Apollo program that would ultimately achieve this monumental goal.
The Apollo program faced numerous challenges, from technological hurdles to budget constraints, yet it persevered, driven by the determination to achieve the impossible. The program consisted of a series of missions, each building on the successes and lessons learned from its predecessors. The groundwork laid by these missions was crucial in ensuring the success of Apollo 11, the mission that would finally see man set foot on the moon. The culmination of years of research, innovation, and dedication was about to be realized in one of humanity's greatest achievements.
How Did the Space Race Intensify?
The space race between the United States and the Soviet Union intensified significantly during the 1960s, as both nations aimed to demonstrate their technological and ideological superiority. This competition extended beyond mere scientific exploration; it was a battle for dominance on the global stage. The Soviet Union's early successes, such as the first manned spaceflight by Yuri Gagarin in 1961, posed a significant challenge to the United States, spurring them to accelerate their efforts in space exploration.
The United States responded by increasing its investment in space technology and research, establishing NASA as the leading agency for space exploration. The Apollo program was launched with the ambitious goal of landing a man on the moon, a task that required unprecedented levels of innovation and collaboration. This era saw rapid advancements in spacecraft design, propulsion systems, and navigation technologies, as the two superpowers raced to achieve the ultimate prize: a successful manned mission to the moon.
As the space race progressed, it became clear that more than technological prowess was at stake. The moon landing represented a symbolic victory in the broader geopolitical struggle between the United States and the Soviet Union. It was a demonstration of national pride and a testament to the power of human ingenuity. Despite the intense rivalry, the moon landing ultimately became a shared triumph for humanity, showcasing what could be achieved through determination and collaboration.
Read also:Gary Watson Garden Gner Your Guide To A Flourishing Landscape
The Apollo 11 Mission: A Closer Look
The Apollo 11 mission, launched on July 16, 1969, was a pivotal moment in space exploration history. The mission was the culmination of years of research, development, and testing, bringing together the brightest minds in science and engineering to achieve a common goal. The spacecraft consisted of three main components: the Command Module (Columbia), the Service Module, and the Lunar Module (Eagle), each playing a crucial role in the success of the mission.
The mission plan was meticulously crafted to ensure the safe landing and return of the astronauts. The journey to the moon involved several critical phases, including the launch, trans-lunar injection, lunar orbit insertion, and the lunar landing itself. Each phase required precise calculations and flawless execution, as any deviation could have jeopardized the mission's success. The astronauts underwent rigorous training to prepare for the challenges they would face, from operating the spacecraft to conducting experiments on the lunar surface.
The moment when the Lunar Module touched down on the moon's surface was a triumph of human achievement and perseverance. The successful landing was broadcast live to an audience of millions, capturing the world's attention and igniting a sense of wonder and curiosity about the possibilities of space exploration. The mission's success was a testament to the dedication and ingenuity of all those involved, from the astronauts who bravely ventured into the unknown to the countless individuals who worked tirelessly behind the scenes.
Who Were the Crew Behind the Moon Landing?
The success of the Apollo 11 mission was made possible by the dedicated and skilled crew who embarked on this historic journey. The mission's commander, Neil Armstrong, was joined by Command Module Pilot Michael Collins and Lunar Module Pilot Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin. Each member of the crew played a vital role in the mission's success, bringing their expertise and experience to the forefront of this ambitious endeavor.
Neil Armstrong, as the mission commander, was responsible for the overall success of the mission. With a background in aeronautical engineering and extensive experience as a test pilot, Armstrong's leadership and calm demeanor were crucial in navigating the challenges of the mission. His historic first step on the lunar surface marked a defining moment in human history, symbolizing the culmination of years of effort and dedication.
Buzz Aldrin, the Lunar Module Pilot, was responsible for the operation of the Lunar Module during its descent and ascent from the moon's surface. Aldrin's expertise in orbital mechanics and his meticulous attention to detail were instrumental in ensuring the success of the lunar landing. His contributions extended beyond the mission itself, as he played a key role in the development of the docking and rendezvous techniques used in the Apollo program.
Michael Collins, the Command Module Pilot, remained in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon's surface. Collins was responsible for piloting the Command Module and ensuring its safe return to Earth. His role was critical in the success of the mission, as he maintained communication with mission control and provided support to his fellow astronauts on the lunar surface. Together, the crew's dedication, expertise, and teamwork were pivotal in achieving the monumental goal of landing a man on the moon.
What Happened When Man Stepped on the Lunar Surface?
The moment Neil Armstrong stepped onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, was a defining moment in human history. As he descended the ladder of the Lunar Module, Armstrong uttered the now-iconic words, "That's one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind," capturing the profound significance of the achievement. This moment, broadcast live to an audience of millions, marked humanity's first steps on an extraterrestrial body and symbolized the triumph of human ingenuity and perseverance.
During their time on the moon, Armstrong and Aldrin conducted a series of experiments and collected samples of lunar soil and rocks. These samples provided valuable insights into the moon's composition and geological history, contributing to our understanding of the solar system. The astronauts also deployed scientific instruments, including a seismometer and a solar wind experiment, to gather data on the moon's environment.
The exploration of the lunar surface was not without its challenges. The astronauts had to navigate the harsh and unfamiliar terrain while wearing bulky space suits, carefully managing their limited time and resources. Despite these challenges, Armstrong and Aldrin successfully completed their objectives, leaving a lasting legacy of exploration and discovery. Their achievements paved the way for future missions and inspired generations to reach for the stars, igniting a sense of wonder and curiosity about the possibilities of space exploration.
Technological Advancements from the Moon Landing
The moon landing was not only a monumental achievement in human exploration but also a catalyst for technological advancements that continue to benefit society today. The Apollo program spurred innovation across various fields, leading to the development of new technologies and materials that have found applications beyond space exploration.
One of the most significant technological advancements to emerge from the moon landing was the development of computer technology. The Apollo Guidance Computer, used to navigate the spacecraft, was one of the first computers to employ integrated circuits, laying the groundwork for the development of modern computing technology. The advances made in computing during the Apollo program have had a profound impact on numerous industries, from telecommunications to healthcare and beyond.
The moon landing also led to advancements in materials science, as the development of lightweight and durable materials was essential for the success of the mission. These materials, originally designed for use in spacecraft, have since found applications in various industries, including aviation, automotive, and consumer electronics. The innovations in materials and manufacturing processes have contributed to the development of more efficient and sustainable technologies.
In addition to technological advancements, the moon landing also spurred interest and investment in scientific research and education. The success of the Apollo program inspired a generation of scientists and engineers, leading to increased funding for research and development in fields such as astronomy, physics, and engineering. The legacy of the moon landing continues to influence scientific exploration and innovation, driving progress and discovery in the pursuit of knowledge and understanding.
Impact on Space Exploration and Beyond
The moon landing had a profound impact on space exploration, shaping the direction of future missions and inspiring a renewed interest in the pursuit of scientific discovery. The success of Apollo 11 demonstrated the feasibility of manned space exploration, paving the way for subsequent missions to the moon and beyond. The knowledge and experience gained from the Apollo program have been instrumental in the development of modern space exploration efforts, from the International Space Station to plans for future missions to Mars and beyond.
The moon landing also had a significant impact on international collaboration in space exploration. While the space race was initially characterized by competition between the United States and the Soviet Union, the success of the Apollo program highlighted the potential for cooperation in the pursuit of common goals. This spirit of collaboration has continued to shape space exploration efforts, with countries around the world working together on projects such as the International Space Station and the Artemis program, which aims to return humans to the moon.
Beyond its impact on space exploration, the moon landing also had broader implications for society as a whole. It inspired a sense of wonder and curiosity about the universe, encouraging people to dream big and strive for the seemingly impossible. The achievements of the Apollo program continue to serve as a reminder of the power of human ingenuity and perseverance, inspiring future generations to push the boundaries of what is possible and explore the unknown.
The Lasting Legacy of the Moon Landing
The legacy of the moon landing extends far beyond the achievements of the Apollo program, leaving a lasting impact on science, technology, and society. The success of the mission demonstrated the power of human innovation and collaboration, proving that even the most ambitious goals can be achieved through determination and perseverance. The spirit of exploration and discovery that defined the Apollo program continues to inspire and motivate future generations to reach for the stars.
The moon landing also served as a catalyst for advancements in technology and science, driving progress and innovation across various fields. The breakthroughs made during the Apollo program have had lasting implications, from the development of modern computing technology to advancements in materials science and engineering. These innovations continue to benefit society today, contributing to the development of more efficient and sustainable technologies.
Beyond its technological and scientific impact, the moon landing also left an indelible mark on culture and society. It inspired a sense of wonder and curiosity about the universe, encouraging people to dream big and strive for the seemingly impossible. The achievements of the Apollo program serve as a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the potential for future exploration and discovery.
Are There Moon Landing Conspiracy Theories?
Despite the overwhelming evidence supporting the authenticity of the moon landing, various conspiracy theories have emerged over the years, questioning the legitimacy of the Apollo 11 mission. These theories often claim that the moon landing was staged by the United States government as part of a broader effort to win the space race and assert technological superiority over the Soviet Union.
Common arguments put forth by conspiracy theorists include claims of inconsistent shadows in photographs, the absence of stars in lunar surface images, and the waving of the American flag in a vacuum. However, these claims have been thoroughly debunked by experts and scientists, who have provided logical explanations for each of these phenomena. For example, the absence of stars in lunar images is due to the camera settings used to capture the brightly lit lunar surface, while the flag's movement is explained by the astronauts' handling and the lack of atmospheric resistance.
The moon landing conspiracy theories persist despite the wealth of evidence supporting the mission's authenticity, including rock samples, telemetry data, and testimony from thousands of individuals involved in the Apollo program. These theories often lack credible evidence and rely on misunderstandings of scientific principles. The continued belief in such theories highlights the importance of critical thinking and the need to rely on credible sources and scientific evidence when evaluating claims.
How Did the Moon Landing Influence Education and Science?
The moon landing had a significant impact on education and science, inspiring a renewed interest in space exploration and scientific discovery. The success of the Apollo program captured the imagination of people around the world, encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. The achievements of the Apollo program demonstrated the power of human ingenuity and collaboration, inspiring future generations to explore the unknown and push the boundaries of what is possible.
The moon landing also led to increased funding and investment in scientific research and education, driving progress and innovation across various fields. The success of the Apollo program highlighted the importance of STEM education and the need for a skilled workforce to support future exploration efforts. This emphasis on education and research has contributed to the development of new technologies and scientific advancements, benefiting society as a whole.
In addition to its impact on education and research, the moon landing also served as a catalyst for public outreach and engagement in science. The success of the Apollo program inspired a sense of wonder and curiosity about the universe, encouraging people to learn more about space exploration and scientific discovery. This increased interest in science and exploration has had a lasting impact, fostering a culture of curiosity and innovation that continues to drive progress and discovery.
When Are Moon Landing Anniversaries Celebrated?
The anniversary of the moon landing is celebrated annually on July 20th, commemorating the day in 1969 when Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin became the first humans to set foot on the lunar surface. This milestone is celebrated around the world, serving as a reminder of the remarkable achievements of the Apollo program and the power of human ingenuity and perseverance.
The moon landing anniversary is often marked by events and activities that celebrate the legacy of the Apollo program and its impact on science, technology, and society. These celebrations may include public lectures, educational programs, and exhibitions showcasing the achievements of the Apollo program and the advancements in space exploration that have followed. The anniversary also serves as an opportunity to reflect on the future of space exploration and the potential for further discovery and innovation.
In addition to the annual celebrations, significant anniversaries of the moon landing, such as the 50th anniversary in 2019, are often marked by larger-scale events and initiatives. These milestones serve as opportunities to highlight the achievements of the Apollo program and inspire future generations to continue exploring the unknown and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
What Does the Future Hold for Moon Missions?
The success of the Apollo program laid the foundation for future exploration efforts, and the moon remains a key focus of ongoing and upcoming space missions. The renewed interest in lunar exploration is driven by the potential for scientific discovery, technological advancements, and the establishment of a sustainable human presence on the moon.
Future moon missions are being planned by a range of countries and organizations, each with their own goals and objectives. NASA's Artemis program aims to return humans to the moon by the mid-2020s, with the goal of establishing a sustainable presence on the lunar surface. This program will build on the achievements of the Apollo program, leveraging new technologies and international collaboration to explore the moon's surface and conduct scientific research.
In addition to NASA's efforts, other countries, including China, India, and the European Space Agency, are also planning lunar missions with a focus on scientific exploration and resource utilization. These missions will explore the potential for mining lunar resources, such as water ice, which could support future exploration efforts and contribute to the development of a sustainable lunar economy.
The future of moon missions holds great promise for scientific discovery and technological advancement. The exploration of the moon will provide valuable insights into the history and evolution of the solar system, while the development of new technologies and resources will drive progress and innovation. The legacy of the Apollo program continues to inspire and motivate future generations to reach for the stars and explore the unknown.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why was the moon landing significant?
The moon landing was significant because it marked the first time humans set foot on an extraterrestrial body, showcasing the power of human ingenuity and perseverance. It was a pivotal moment in space exploration history and a symbol of national pride during the space race between the United States and the Soviet Union.
2. How did the moon landing impact technology?
The moon landing spurred technological advancements across various fields, including computing, materials science, and telecommunications. The development of the Apollo Guidance Computer laid the groundwork for modern computing technology, while innovations in materials science have found applications beyond space exploration.
3. What were the main objectives of the Apollo 11 mission?
The main objectives of the Apollo 11 mission were to land humans on the moon and return them safely to Earth. The mission also aimed to conduct scientific experiments and collect samples of lunar soil and rocks to gain insights into the moon's composition and geological history.
4. How did the moon landing influence education?
The moon landing inspired a renewed interest in STEM education, encouraging students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. It also led to increased funding and investment in scientific research and education, driving progress and innovation across various fields.
5. Are moon landing conspiracy theories legitimate?
Moon landing conspiracy theories lack credible evidence and have been thoroughly debunked by experts and scientists. The wealth of evidence supporting the authenticity of the moon landing, including rock samples, telemetry data, and testimony from individuals involved in the Apollo program, supports its legitimacy.
6. What are the goals of future moon missions?
Future moon missions aim to establish a sustainable human presence on the moon, conduct scientific research, and explore the potential for resource utilization. Programs like NASA's Artemis seek to return humans to the moon by the mid-2020s and leverage international collaboration to achieve these goals.
Conclusion
The moon landing remains one of humanity's most remarkable achievements, symbolizing the triumph of human ingenuity and the power of collaboration and determination. The success of the Apollo 11 mission marked a pivotal moment in space exploration history, inspiring generations to reach for the stars and explore the unknown. The legacy of the moon landing continues to influence science, technology, and society, driving progress and innovation across various fields.
As we look to the future, the renewed interest in lunar exploration promises to unlock new opportunities for scientific discovery and technological advancement. The achievements of the Apollo program serve as a testament to what can be accomplished through perseverance and collaboration, inspiring future generations to dream big and strive for the seemingly impossible. The exploration of the moon and beyond holds great promise for the future of humanity, offering a glimpse into the possibilities of exploration and discovery.
For further information on the moon landing and its impact on science and technology, visit NASA's Apollo 11 page.